The environmental crisis has drawn people?s interest in alternative energy sources. In the last decade, the most investment in PV manufacturing was seen in some of the major world powers such as the United States, China, Europe, and Japan.
Only between 2006 and 2007, there was a 50-percent increase in cumulative installed capacity reaching approximately 7.7GW.
Nonetheless, there are a few bumps on the road for solar energy development projects. While solar energy and other renewable energy systems have shown improvement during the past decades, some global factors threatened this growth.
Before the Covid-19 pandemic, Rystad Energy predicted a 140-gigawatt addition in the industry in 2020. This corresponded to a steady growth history of 15% on a year-to-year basis.
Nonetheless, the pandemic hit, and the landscape changed completely. Back in March 2020, experts predicted a harsh period for renewable-source projects. On the verge of what may be the highest recession in modern history, the outlook for innovative enterprises did not look good.
During a recession, several factors affect the PV manufactory industry and the solar energy projects in general.
Factors and conditions that affect the PV manufacturing industry
Lack of financing
During a recession, the liquidity levels are lower, hence the market shrinks. With less liquidity out there, there is less money to be put into projects. Moreover, investors tend to move their allocations into safe assets like fixed-income vehicles withdrawing their investments from riskier industries.
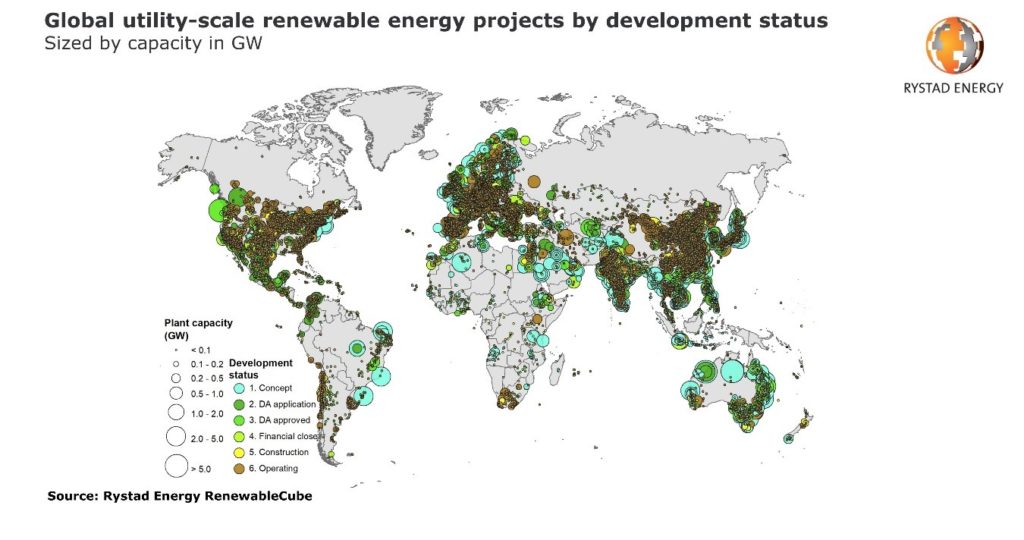
Low electricity demand
As large investors tend to be cautious and withdraw their capital from less traditional markets, average citizens tend to spend less. This impacts energy consumption (like shown in the chart below) hence affects energy markets.
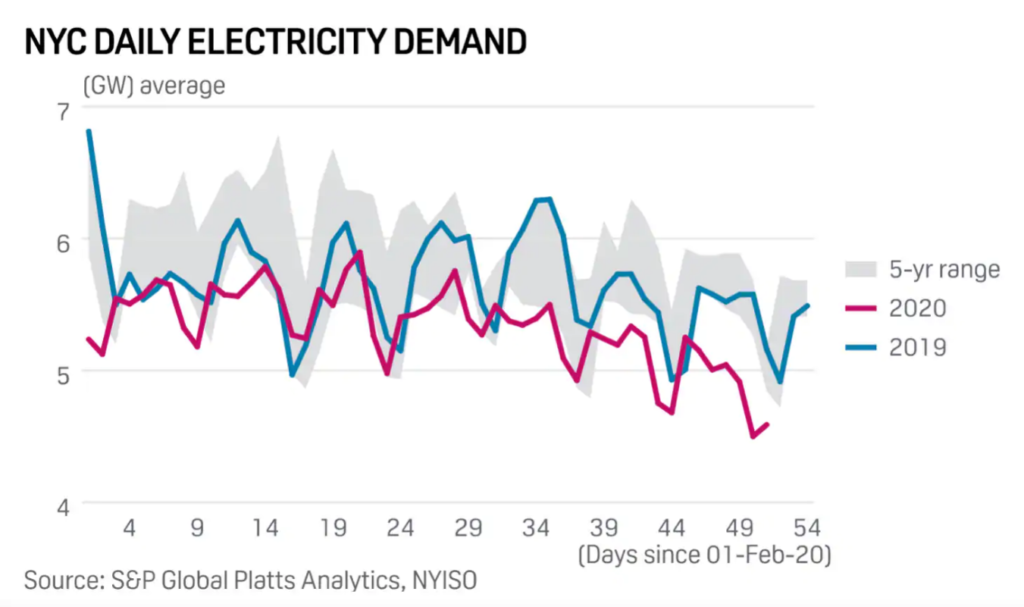
Although the renewable energy sector is protected by PPAs (Power Purchase Agreements), these prices are usually higher than market prices, which can also draw investors away.
Stranded projects
In line with the previous point, small or newly released projects may never see the light of day. Financing is arguably impossible to get in such a context and, even if self-financed, a project owner may find other challenges. The cost of the materials increases and is usually in US dollars, which makes it difficult for projects that work with other currencies. In a recession, currency volatility can make it impossible for a project to face exchange costs.
This has been worsened during the coronavirus crisis due to transportation restrictions that generate even greater costs and involve delays.
Sources indicate that, since March 2020, there was a shortage of materials like inverters and modules which resulted in a 15-percent increase in prices.
The renewable energy industry during the Covid-19 pandemic
Besides the negative predictions, the renewable energy industry is throwing good results in 2021. In April, the IRENA (International Renewable Energy Agency) released encouraging reports. IRENA?s statistics show an increase in new generating capacity for the second year in a row. It reports a growth of 260 gigawatts in renewable energy capacity in 2020, exceeding 2019 almost by half.
This increase has taken place partly due to the underperformance of the fuel-energy sector. There was a net decommissioning of fossil power generation in Europe, North America, and Eurasia. This sector saw a decrease from 64 GW to 60 GW in 2020, in line with an overall bearish tendency.
Solar energy, in particular, is a worthy player in this increasing curve. It has reached nearly the same level as wind capacity. This is thanks to the expansion in Asian countries with a 45 GW increase in China and 11 GW in Vietnam. Japan added 5 GW while India and Korea added 4 GW. The United States increased its capacity by adding 15 GW.

Total solar capacity has reached practically the same level as wind capacity in 2020
PV module manufacturers, the most important industry players in 2020
The PV manufacturing industry has shown interesting tendencies. For a while now, a small group of players has controlled the polysilicon and monocrystalline wafer manufacturing. This consolidation is still growing, and this is reflected in statistics from the past years.
The market for module and cell construction has been historically more fragmented, however, this tendency is changing. While smaller participants used to take part in this niche, in 2020, their involvement seemed to be decreasing.
Some of the Chinese biggest players in the industry are taking over the module and cell construction markets. This is partly because the industry is gradually starting to use larger wafer formats, hence, small companies cannot afford the building costs. This opens the way for the PV industry giants, who have the means to build the wafers that the current market demands.
The next section presents an analysis of today?s PV manufacturing industry and how to evaluate the manufacturers? competency in this context.
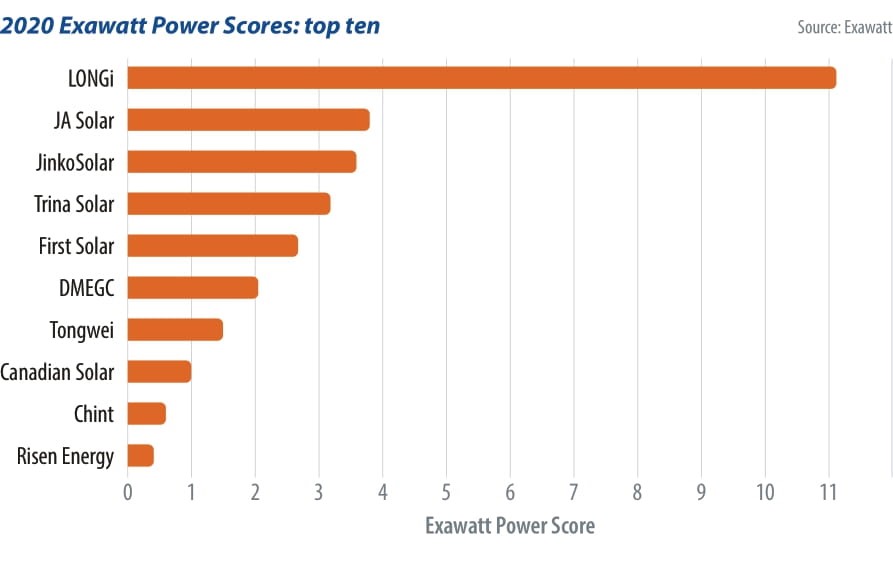
The graphic shows the top ten PV manufacturers in 2020 according to Exawatt
How to measure and compare PV module manufacturers?
But how do we compare different market players based on parameters other than capacity and shipment? Fortunately, Exawatt has developed a ranking (Exawatt?s Power Score and Power Ranking) to compare different module builders in the market. Nonetheless, a company?s place in this ranking does not necessarily reflect the quality of its products.
The ranking is based on three parameters: PV presence, financial health, and profitability.
Exawatt?s Power Source and Power rankings parameters
- PV presence:
